Introduction
Passive heat sinks play a crucial role in the thermal management of electronic devices, LED lighting, automotive systems, and various other applications where heat dissipation is vital. Unlike active heat sinks that rely on external power to function, passive heat sinks work through natural convection, making them energy-efficient and noiseless cooling solutions. In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of passive heat sinks, their working principles, advantages, limitations, and their applications in different industries.
What is a Passive Heat Sink?

A passive heat sink is a cooling device designed to dissipate excess heat generated by electronic components without the need for any external power source. It operates based on the principles of natural convection, where heat flows from a higher temperature area to a lower temperature area. Heat sinks are typically made of materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminium or copper, and consist of fins or ridges that increase the surface area for better heat dissipation.
How Does a Passive Heat Sink Work?
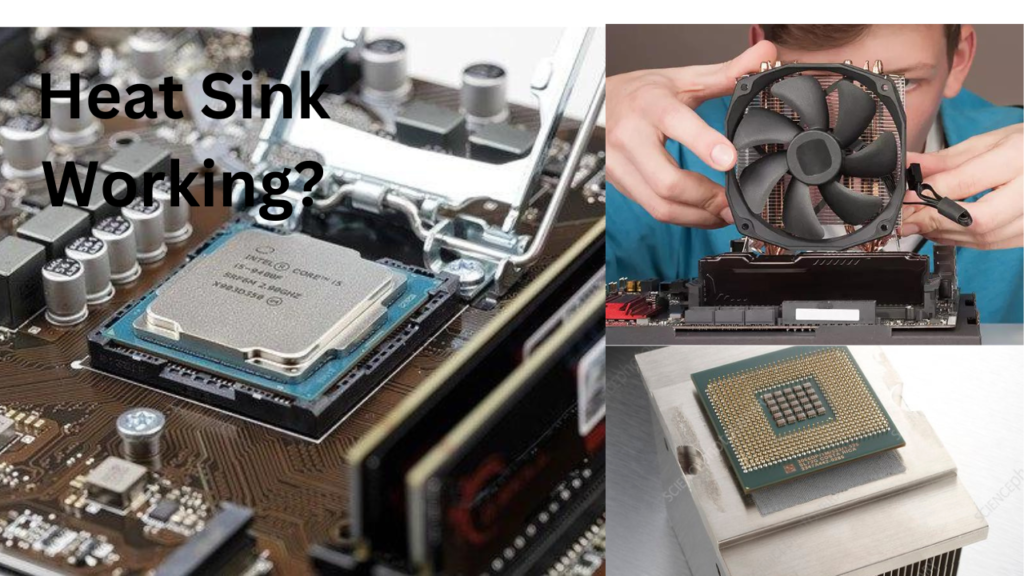
When electronic components, such as CPUs or GPUs, generate heat during operation, that heat is transferred to the heat sink. The heat sink then passively conducts the heat away from the component and spreads it across its fins. As the surrounding air comes into contact with the heat sink’s fins, it absorbs the heat and rises, creating a natural airflow that carries the heat away from the device.
Advantages of Passive Heat Sinks

Silent Operation: One of the most significant advantages of heat sinks is their silent operation. Since they do not require any fans or moving parts, there is no noise generated during the cooling process. This makes heat sinks ideal for applications where noise reduction is essential, such as in audio equipment or home theatre systems.
Zero Power Consumption: These heat sinks do not consume any power as they rely solely on natural convection for cooling. This results in lower energy consumption and contributes to overall energy efficiency in electronic devices and systems.
Reliability and Longevity: These heat sinks have a simple and robust design, which leads to enhanced reliability and longevity. With no mechanical components to wear out, they have a longer lifespan compared to active cooling solutions.
Limitations of Passive Heat Sinks
Less Efficient than Active Heat Sinks: While passive heat sinks are effective for moderate heat dissipation, they are generally less efficient than active heat sinks in handling high heat loads. In applications with extreme heat conditions, an active cooling solution may be more suitable.
Limited Heat Dissipation Capacity: These heat sinks’ cooling capacity is limited by the available airflow and natural convection. In environments with restricted airflow, their performance may be compromised.
Ineffectiveness in High-Temperature Environments: These heat sinks may struggle to dissipate heat effectively in environments with extremely high ambient temperatures. In such cases, supplementary cooling methods might be required.
Types of Passive Heat Sinks

Passive heat sinks come in various types, each designed for specific applications and cooling requirements:
Stamped Heat Sinks: These are cost-effective heat sinks created through a stamping process, suitable for lower heat dissipation needs.
Extruded Heat Sinks: Extruded heat sinks are produced by pushing aluminium or other materials through a die, creating fins in a single piece. They are versatile and find applications across a wide range of industries and electronic devices.
Forged Heat Sinks: Forged heat sinks offer superior thermal conductivity and are ideal for high-performance applications.
Bonded Fin Heat Sinks: Bonded fin heat sinks have fins that are bonded to a base, providing efficient heat transfer.
Materials Used in Passive Heat Sinks

Aluminum Heat Sinks: Aluminum is the most commonly used material for passive heat sinks due to its lightweight, good thermal conductivity, and cost-effectiveness.
Copper Heat Sinks: Copper heat sinks offer excellent thermal conductivity and are particularly suitable for high-performance cooling applications.
Aluminum Alloy Heat Sinks: Aluminum alloys provide a balance between thermal performance and cost, making them popular choices for various cooling needs.
Other Materials: In some cases, passive heat sinks are made of materials like graphite or ceramic for specialized applications.
Applications of Passive Heat Sinks
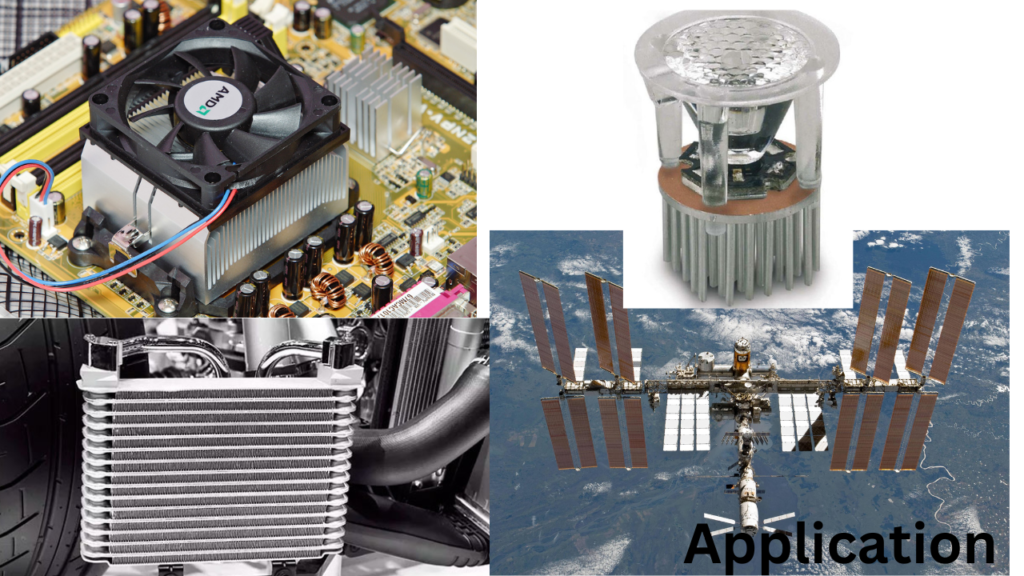

Electronics and Computers: Passive heat sinks are extensively used in electronic devices such as CPUs, GPUs, motherboards, and other components to prevent overheating and ensure reliable performance.
LED Lighting: LED lights generate heat during operation, and passive heat sinks are used to keep the temperature within acceptable limits, prolonging the life of the LEDs.
Automotive: Passive heat sinks play a crucial role in cooling electronic components in vehicles, ensuring proper functionality and preventing failures due to excessive heat.
Aerospace: In aerospace applications, passive heat sinks are used to cool avionics and electronic systems on aircraft and satellites, ensuring reliable operation in extreme conditions.
Design Considerations for Passive Heat Sinks
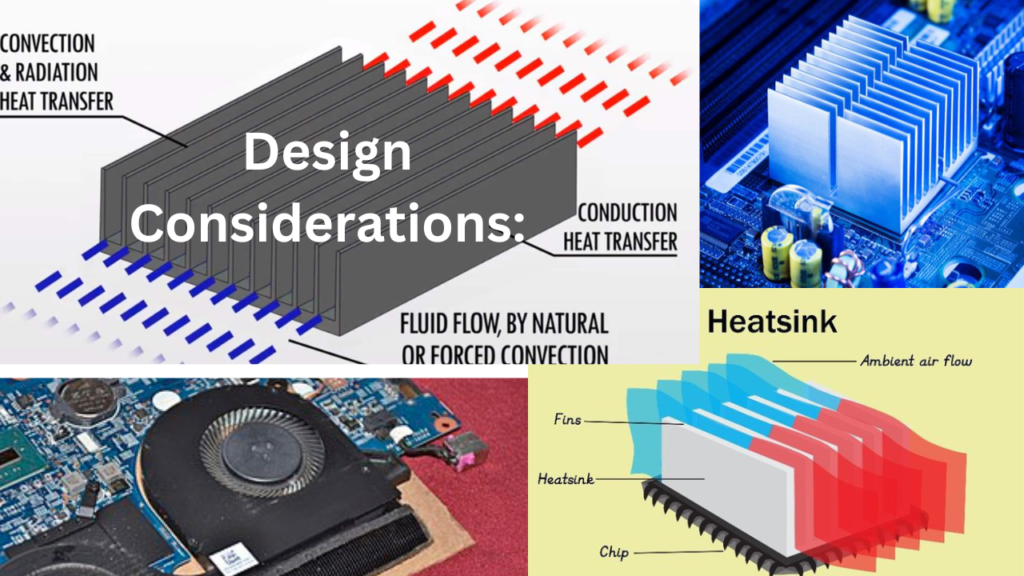
Surface Area and Fins: The surface area and the number of fins on a heat sink significantly impact its cooling efficiency. More fins and a larger surface area facilitate better heat dissipation.
Thermal Interface Materials: Proper selection of thermal interface materials, such as thermal paste or pads, is essential for optimizing heat transfer between the heat sink and the electronic component.
Airflow and Natural Convection: Adequate airflow is critical for effective heat dissipation. Proper design and placement of the heat sink can enhance natural convection for better cooling.
Heat Sink Orientation: Mounting orientation can influence the heat sink’s performance. Correctly aligning the heat sink with the airflow direction ensures optimal cooling.
Installation and Maintenance of Passive Heat Sinks
Correct Mounting Techniques: Properly installing the passive heat sink is essential to ensure good thermal contact and efficient heat transfer. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines is crucial.
Cleaning and Dust Removal: Regularly cleaning the heat sink and removing accumulated dust or debris improves its cooling efficiency and prolongs its lifespan.
Periodic Inspection: Periodically checking the heat sink for any signs of damage or deterioration helps maintain its effectiveness.
Passive Heat Sinks vs. Active Heat Sinks
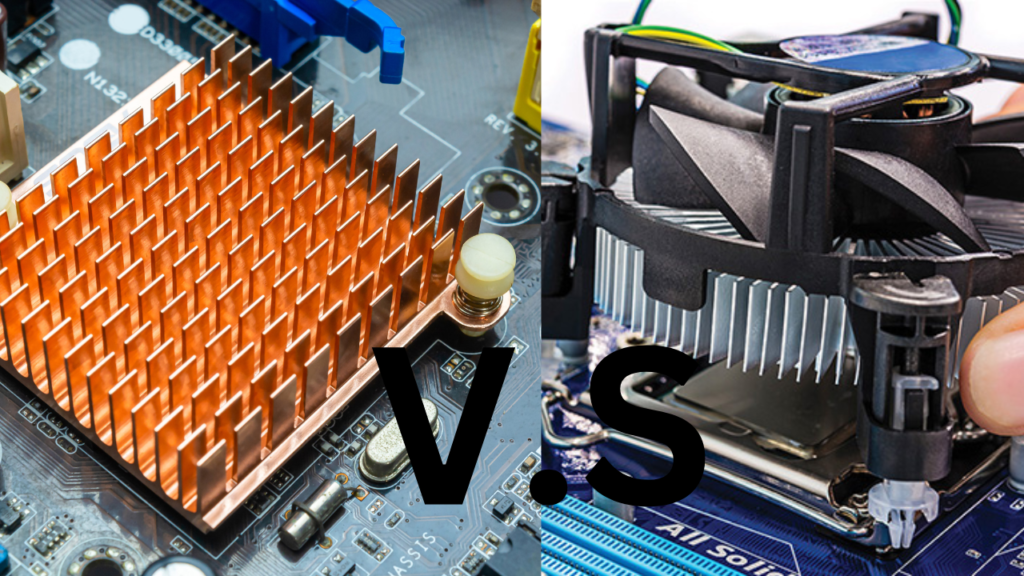
Different Working Principles: The primary difference between passive and active heat sinks lies in their working principles. Passive heat sinks rely on natural convection, while active heat sinks use fans or pumps for forced convection.
Selecting the Right Heat Sink for Your Needs: The choice between passive and active heat sinks depends on the specific cooling requirements, heat loads, and environmental conditions of the application.
Future Trends in Passive Heat Sink Technology
Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Techniques: Ongoing advancements in materials and manufacturing processes will lead to even more efficient and lightweight passive heat sinks.
Passive Heat Sinks in IoT and Edge Computing: With the proliferation of IoT devices and edge computing, passive heat sinks will play a vital role in cooling these compact and interconnected systems.
Integration with Other Cooling Solutions: Passive heat sinks will likely be integrated with other cooling technologies to create hybrid cooling solutions for enhanced efficiency.
Conclusion
Passive heat sinks offer an energy-efficient and silent solution for cooling electronic components and various other applications. With their simple and reliable design, they are widely used in the electronics, automotive, aerospace, and lighting industries. Properly selecting, installing, and maintaining passive heat sinks is essential for optimal cooling performance and extended component lifespan.
FAQs
1. How do passive heat sinks cool electronic devices?
Passive heat sinks cool electronic devices by absorbing and dissipating heat through natural convection, providing silent and energy-efficient cooling.
2. Are passive heat sinks suitable for overclocking?
While passive heat sinks can handle moderate heat loads, they may not be ideal for extreme overclocking scenarios that require more robust cooling solutions.
3. Can I use a passive heat sink for high-performance gaming PCs?
Passive heat sinks are not recommended for high-performance gaming PCs that generate significant heat. Active cooling solutions are more suitable for such setups.
4. How do I choose the right passive heat sink for my application?
Consider factors such as the heat load, available airflow, and required cooling capacity to select the appropriate passive heat sink for your specific application.
5. Are passive heat sinks environmentally friendly?
Yes, passive heat sinks are environmentally friendly due to their energy-efficient and fanless design, which reduces power consumption and e-waste.